Cortisol Imbalance: Exploring Symptoms, Effects, and Management
Cortisol, known as the “stress hormone, plays a crucial role in our body’s response to challenging situations. However, when cortisol levels become imbalanced, it can lead to a range of symptoms and disruptions in our overall well-being. From symptoms of high cortisol levels to the impact of cortisol in your blood, comprehending the complexities of cortisol imbalance is essential for maintaining optimal health.
In times of stress or perceived threat, our body’s natural response triggers the release of cortisol, preparing us for the famous “fight or flight” response. This hormone not only mobilizes our energy reserves but also influences various physiological processes. However, an excess of cortisol can have adverse effects, including increased blood pressure and other symptoms associated with high cortisol levels.
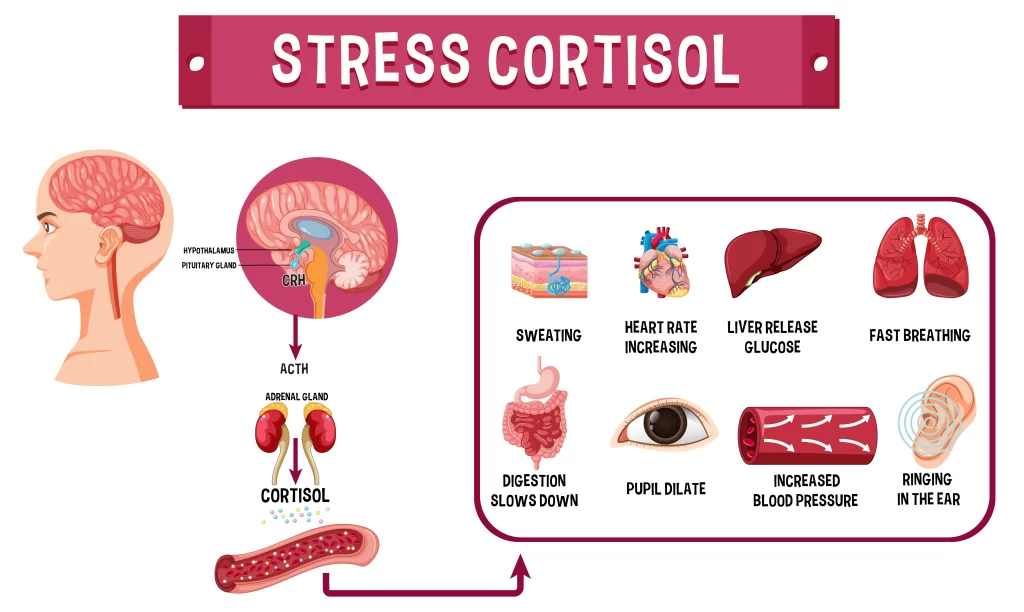
The intricate regulation of cortisol involves the corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) secreted by the hypothalamus, which signals the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Subsequently, the adrenal glands release cortisol into the bloodstream. Imbalances in this delicate system can disrupt the proper functioning of cortisol and contribute to health issues, such as chronic stress, and anxiety, and even cause low blood pressure in some cases.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of cortisol imbalance is pivotal in identifying its causes, effects, and potential interventions. In this article, we delve deeper into the symptoms of high cortisol, explore the role of cortisol in your blood, and examine the intricate mechanisms involving the corticotrophin-releasing hormone. By shedding light on this important aspect of our body’s stress response system, we aim to provide valuable insights for managing and maintaining cortisol balance.
Key Takeaway:
- Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that helps regulate stress response, metabolism, inflammation, blood pressure, blood sugar, and sleep-wake cycle. An imbalance in cortisol levels can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, anxiety, insomnia, weight gain, and depression.
- Causes of cortisol imbalance can include chronic stress, poor sleep, unhealthy diet, physical illness, medication, and hormonal disorders. Diagnosis of cortisol imbalance can be done through blood or saliva testing.
- Treatment options for cortisol imbalance usually involve lifestyle changes such as stress management, healthy diet and exercise, and supplements. In severe cases, medical interventions such as corticosteroids may be necessary.
Understanding Cortisol
Cortisol – the stress hormone, is a key player in our body’s stress response, with a long list of functions that contribute to our overall well-being. In this segment, we will be diving deeper into the world of Cortisol, understanding its definition, function, and the importance of homeostasis.
Cortisol plays a critical role in balancing our body’s physiological systems and regulating key functions, ranging from blood sugar levels to immune system responses. We will explore how an imbalance in cortisol can cause a wide range of symptoms, and how maintaining a balanced cortisol level is critical for optimal health.
Definition and Function
Cortisol has both a definition and a function in the body. It is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland and serves important roles in homeostasis. Homeostasis refers to the ability of living organisms to maintain a stable internal environment amid changing external conditions. Cortisol helps regulate the stress response, metabolism, inflammation, blood pressure, blood sugar, and sleep-wake cycle.
As a stress hormone, cortisol plays a crucial role in responding to different types of stressors that an organism encounters. These can be physical, emotional, or even psychological. Upon experiencing a stressor, cortisol levels rise as part of the fight or flight response. This increases the energy and focus needed to deal with the perceived threat.
Cortisol signals different organ systems throughout the body to prepare for action during times of stress. In addition to this acute response to stressors, it has longer-term effects on metabolism and immune function. Specifically, cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis (the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources) and elevates blood pressure and heart rate when necessary.
If there is an imbalance in cortisol levels within the body either too high or low levels this can lead to several symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain/loss, sleep disturbances/anxiety/depression etc). The causes may be due to several factors including chronic stress or disease.
To diagnose cortisol imbalances physicians generally use various methods such as the Salivary Cortisol test & ACTH stimulation test under medical guidance and depending upon which level fluctuates they suggest lifestyle changes or provide medication accordingly.
In order not to miss out on your health and well-being it’s recommended that you be aware – both physically & mentally- when experiencing symptoms associated with cortisol imbalance such as fatigue, anxiety, or depression accompanied by stressful events & seek medical advice at the earliest opportunity.
Without homeostasis, our bodies would be as chaotic and unpredictable as an episode of Keeping Up With The Kardashians.
Importance of Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment is crucial for the longevity of living organisms. One such mechanism that ensures this stability is called homeostasis, which plays a critical role in regulating various bodily functions, including body temperature, blood pressure, and fluid balance. The importance of homeostasis lies in its ability to maintain optimal physiological conditions required for normal cellular function and overall well-being.
In particular, homeostasis is essential for the proper functioning of the endocrine system and hormones like cortisol. Cortisol levels are tightly regulated through negative feedback mechanisms to ensure bodily functions remain stable during times of stress or illness. Without homeostasis, disruptions in cortisol levels could lead to imbalances that may cause long-term health complications.
While we’ve covered the basic importance of homeostasis above, it’s worth noting that this biological process is important not just on an individual level but on a larger societal scale as well. Diseases like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease arise when regular physiological processes go awry because of ubiquitous environmental factors that disrupt the maintenance of metabolic equilibrium.
So it’s clear: Homeostasis isn’t something we can take lightly or ignore without consequence. We must appreciate its importance in fostering healthy life across all domains — physical, mental, and social — or risk letting everything fall out of balance altogether.
Stress and cortisol go together like peanut butter and anxiety.
Cortisol as a Stress Hormone
As we explore the intricate world of hormones, Cortisol occupies a prominent position as a stress hormone, with a significant impact on the body’s physiology. Stress has been described as the body’s natural response to a perceived threat, and determining what constitutes stress varies individually. However, the physical manifestation of stress is consistent across the board.
In the upcoming sections, we explore the different types of stress and understand how Cortisol contributes to our response to stress.
Types of Stress
Stress can take various forms and affect individuals differently. Understanding the types of stress is crucial for identifying its root cause and finding effective solutions to manage it.
- Acute Stress: This type of stress occurs when an individual experiences a sudden and intense event, such as an accident or a near-death experience.
- Chronic Stress: This results from long-term problems or unresolved persistent situations such as financial uncertainty and relationship issues.
- Physical Stress: Physical stress can be due to overexertion, injury, or illness. Symptoms might include fatigue, pain, and muscle tension.
- Emotional Stress: Emotional stress often arises from feelings of fear, anger, anxiety, or sadness.
Each type of stress has its unique characteristics and symptoms that require specific interventions and coping mechanisms.
Coping with constant stress requires adopting new behaviors and lifestyle changes that promote wellness. Don’t wait until you’re under immense pressure to start developing healthy habits; make simple adjustments like eating a well-balanced diet – incorporating foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, and minerals magnesium, and drinking water regularly throughout the day. Taking time off to engage in daily physical activity for at least 30 minutes daily helps your body learn to cope better with different types of stress.
Fear of missing out on a healthier life can be distressing but understanding the types of stressful situations can help implement necessary actions towards wellbeing and better coping mechanisms. Start small and focus on introducing healthy practices one step at a time; your future self will thank you for it!
Stressful situations may make you feel like you’re on the verge of a breakdown, but cortisol is there to pick up the pieces and keep you going.

Role of Cortisol in Stress Response
Cortisol plays a crucial role in the body’s stress response system by regulating physiological responses. An increase in cortisol levels helps the body prepare for a fight-or-flight response during acute stressors such as danger or trauma. It activates several processes such as increasing blood pressure, suppressing the immune system, and releasing glucose for energy.
In chronic stressors like work-related stress, depression, or anxiety, prolonged secretion of cortisol can lead to adverse effects on health. Elevated levels of cortisol can result in weight gain, weakened immune system, high blood pressure, or even cognitive impairment.
Unique to its role in stress response, cortisol aids in reducing inflammation and pain perception while suppressing immune activity. Cortisol can also inhibit glycogen synthesis and protein metabolism contributing to decreased muscle mass.
Pro Tip:
- Creating a daily routine that incorporates exercise and relaxation techniques reduces cortisol levels long-term; supplementing with supplements like magnesium citrate further blunts cortisol’s stress-inducing action.
Cortisol: Making you feel like you’re running a marathon even when you’re just sitting on the couch.
Effects of Cortisol on the Body
As someone who has experienced the effects of cortisol imbalance, I know firsthand how it can impact our bodies. In this part of the article, we’ll be dissecting the various effects of cortisol on our body and the role it plays in regulating:
- stress response
- metabolism
- inflammation
- blood pressure
- blood sugar
- sleep-wake cycle
We’ll explore the target organ systems and what happens when our cortisol levels are too low or too high. Understanding the function of cortisol within our bodies can help us identify the symptoms and causes of cortisol imbalance and how to treat them.
Target Organ Systems
Cortisol impacts the various systems of the body, known as the target organ systems. These include the immune system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, gastrointestinal system, and musculoskeletal system. Cortisol plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating stress response in these systems.
In the immune system, cortisol affects cytokine production and inflammation. It also influences T-cell activity and antibody formation. In the cardiovascular system, cortisol regulates blood pressure and heart rate.
Cortisol also impacts metabolism by affecting glucose production and insulin sensitivity in the liver, adipose tissue, and muscle tissue. It also affects fat distribution throughout the body.
Moreover, cortisol influences sleep-wake cycles by altering melatonin secretion patterns in response to stress. It also affects cognitive function by regulating hippocampal activity.
Additionally, prolonged cortisol imbalance can lead to various health issues such as fatigue, anxiety, weight gain or loss, hypertension, or hypotension among others.
It’s essential to understand that proper cortisol balance is crucial for maintaining overall physiological health. So individuals must listen carefully to their bodies if they notice any of these symptoms or related complications and seek medical advice immediately.
Cortisol: the ultimate multitasker, regulating everything from stress to sleep and everything in between.
Role in Regulating Stress Response, Metabolism, Inflammation, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar, and Sleep-Wake Cycle
Cortisol plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including stress response, metabolism, inflammation, blood pressure, blood sugar, and the sleep-wake cycle. Its hormone regulates the body’s ability to manage different types of stress and perform numerous other necessary functions.
| Function | Effects |
| Stress Response | Manages stress response by preparing the body for “fight or flight” |
| Metabolism | Regulates glucose levels and helps control weight gain |
| Inflammation | Helps remove inflammatory agents from the body |
| Blood Pressure | Maintains blood pressure |
| Blood Sugar | Regulates insulin secretion and metabolism |
| Sleep-Wake Cycle | Regulates natural circadian rhythm |
Cortisol is essential in maintaining homeostasis as it ensures that an organism’s internal environment remains stable despite external changes. However, excessive cortisol production due to prolonged stress can lead to cortisol imbalance, resulting in a variety of symptoms such as anxiety, depression, fatigue, and weight gain. To avoid this situation, one must practice stress management techniques such as meditation or seek medical interventions like CBT or medication.
Don’t miss out on understanding the significant role cortisol plays in our bodies. Take action today by improving your stress management techniques before suffering from detrimental consequences that come with cortisol imbalance.
Get ready for a rollercoaster ride because cortisol imbalance symptoms can be wilder than a theme park.
Cortisol Imbalance: What Is It?
Cortisol is a vital hormone that plays a key role in the body’s stress response. However, when its levels exceed the normal range, it can lead to a condition known as cortisol imbalance. This section will take a closer look at cortisol imbalance and its impact on overall health.
Firstly, we will discuss the definition and symptoms that signal cortisol imbalance and provide insights into the range of potential health problems that can arise.
Additionally, we will explore the causes of cortisol imbalance, which can range from stress to underlying medical conditions.
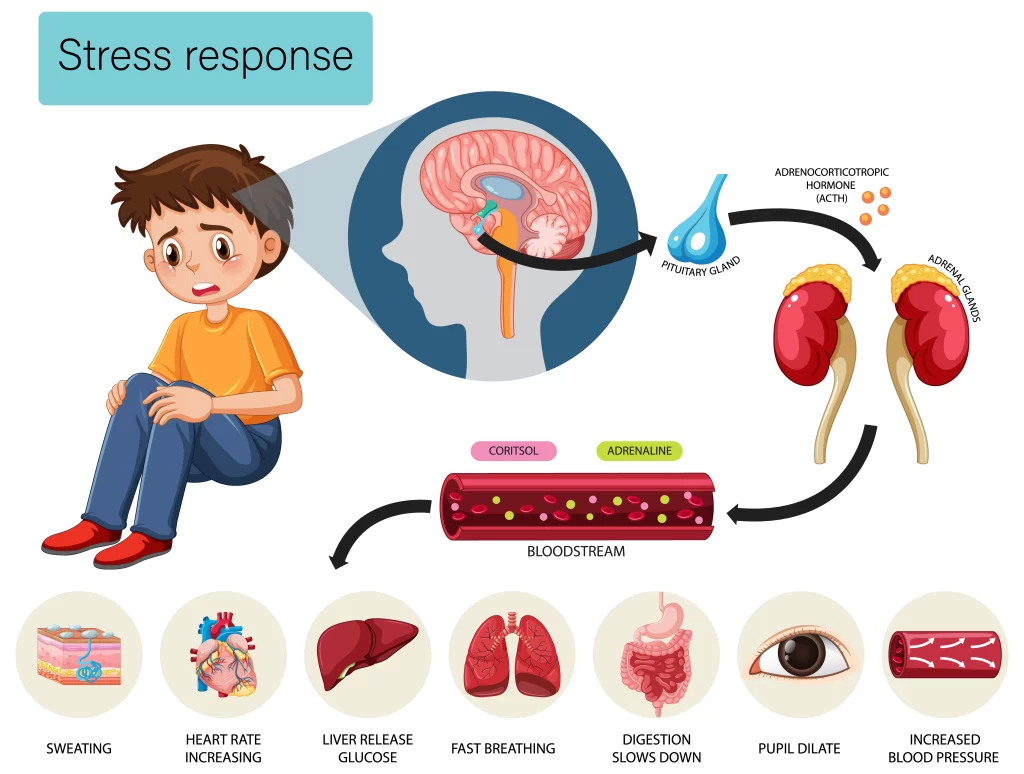
Definition and Symptoms
Cortisol plays a critical role in the body’s response to stress, regulating metabolism, inflammation, blood sugar, blood pressure, and sleep-wake cycles. Cortisol imbalance occurs when the level of cortisol is too high or too low, resulting in various symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain or loss, mood swings, and a weakened immune system.
An increase in cortisol levels causes symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and restlessness whereas a decrease leads to fatigue, weakness, and depression. Cortisol imbalance is caused by various factors such as chronic stress due to work or emotional stressors; unhealthy lifestyle choices like lack of sleep, and poor dietary habits; underlying health conditions like adrenal gland disorders or autoimmune diseases.
It is diagnosed through medical tests that measure cortisol levels in urine or saliva over several days. Normal cortisol levels range from 6-23 mcg/dL in the morning and 2-11 mcg/dL at bedtime.
An individual’s story could be that they experienced a consistent inability to concentrate during an important project despite eating well and getting enough sleep leading them towards seeking medical help for their symptoms. Why blame the cat when it’s actually the stress that’s causing cortisol imbalance?
Causes of Cortisol Imbalance
Excessive stress and lifestyle factors are the primary causes of cortisol imbalance. In addition, prolonged exposure to physical, social, and psychological stressors such as chronic illness, work pressure, and family challenges can contribute to cortisol imbalance. Certain medical conditions like depression, anxiety, and Cushing’s disease can also lead to cortisol imbalance in the body.
Moreover, a lack of sleep, an unhealthy diet, a sedentary lifestyle, and excessive alcohol consumption can significantly disrupt the production of cortisol hormones in the adrenal gland. This hormonal disruption can trigger an irregular circadian rhythm, leading to a cortisol imbalance.
Furthermore, hormonal contraceptives and certain medications like prednisolone may interfere with the normal functioning of the adrenal gland, causing a dysfunctioning feedback mechanism that signals the body to produce more or less cortisol than required.
Studies have shown that long-term exposure to environmental toxins such as lead, pesticides, and plastics compounds could also result in cortisol imbalance. Hence avoiding these substances is highly recommended.
Studies have proven that exposure to an inadequate amount or excess sunlight may severely affect cortisol production too. Therefore medical personnel should advise patients experiencing symptoms associated with this health condition to gradually expose themselves according to advised limits while monitoring their response diligently.
Getting a diagnosis for cortisol imbalance may require some stress-inducing testing, but it’s worth it to understand your body’s functioning.

Diagnosis of Cortisol Imbalance
As I learned more about cortisol imbalance, I realized how critical proper diagnosis is for effective treatment. In this part, we’ll be discussing the diagnosis of cortisol imbalance through two main sub-sections.
- The first sub-section will dive into the most common methods for testing cortisol levels, shedding light on the different procedures used by medical professionals.
- On the other hand, the second sub-section will highlight normal cortisol levels in the body and what ranges can be considered as healthy. It’s vital to get a clear understanding of these crucial factors that determine cortisol imbalance diagnosis.
Methods of Testing Cortisol Levels
Analyzing Cortisol levels in the body requires a number of methods of testing cortisol levels. These range from blood, urine, and saliva tests to dexamethasone suppression test (DST) and corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) stimulation test. Blood tests are the most common method of analyzing cortisol levels as they can be conducted at any time of day. Urine samples, on the other hand, offer reliable results by measuring cortisol metabolites over a 24-hour period. Saliva tests help measure free cortisol concentration throughout the day and avoid the stress experienced while drawing blood.
Interestingly, there is also an exciting research field that utilizes hair analysis to examine long-term cortisol changes in an individual’s body. Studies show that hairs preserve information about all hormonal changes occurring within the human body for up to six months before being cut.
Cortisol imbalances in humans did not always have diagnostic methods at their disposal. Before such tests were developed, people relied on biological indicators such as weight gain, exhaustion, and sleeplessness as signs of imbalance. Luckily, medical progress has made it possible today to recognize cortisol dysfunction with certainty through modern-day testing techniques such as those mentioned above for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Normal cortisol levels: finally something that’s supposed to be average actually is.
Normal Cortisol Levels
Cortisol is a hormone that regulates stress response, metabolism, inflammation, blood pressure, blood sugar, and sleep-wake cycle. Normal cortisol levels vary in individuals and are generally higher in the morning and lower in the evening. However, normal cortisol levels also depend on the age, sex, and overall health of an individual.
If a person’s cortisol levels fall outside of the normal range, it may indicate a cortisol imbalance leading to various symptoms such as fatigue, anxiety, and depression. The diagnosis of cortisol imbalance can be done through various methods such as blood tests or salivary tests.
It is crucial to maintain normal cortisol levels through lifestyle changes like stress management, a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep. Medical interventions may include medications or therapies depending on the severity of the condition.
It is essential to monitor one’s cortisol levels regularly as persistently elevated or reduced levels can lead to long-term health problems like obesity, diabetes, hypertension, etc. Neglecting these issues can put one at risk for serious health consequences – hence seeking immediate medical attention is crucial.
Therefore regular monitoring and maintenance of normal cortisol levels go a long way in maintaining good health and preventing any potential complications.
From meditation to prescription meds, here are the options for balancing out your cortisol.
Treatment Options for Cortisol Imbalance
After understanding the causes and symptoms of cortisol imbalance, it’s essential to start considering the available treatment options. While lifestyle changes and stress management can alleviate mild symptoms, severe cases might require medical interventions and medications. In this section, we will explore the different treatment options available for cortisol imbalances. We’ll start by discussing the effectiveness of lifestyle changes and stress management in treating cortisol imbalance. Then we’ll delve into more complicated treatment methods, such as medical interventions and medications, that may be required in more severe cases. According to the National Institutes of Health, medication may be necessary for individuals with severe symptoms to control cortisol production.
Lifestyle Changes and Stress Management
To mitigate the impact of cortisol imbalance on the body, adopting lifestyle changes and managing stress are effective strategies. Making positive changes in one’s life can significantly reduce cortisol levels. A routine exercise regimen, healthy diet, sufficient sleep, and reduced caffeine intake help balance hormone levels in the body. Moreover, mindfulness practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can reduce stress levels that contribute to cortisol production.
These small daily modifications can have a dramatic effect on one’s emotional well-being and physical health. Engaging in social activities with friends and family or taking up a hobby can likewise alleviate stress caused by daily routines. In addition, avoiding stressful situations or learning how to manage it efficiently goes a long way in reducing cortisol levels.
It is essential to note that there are multiple factors causing hormonal imbalances beyond an individual’s control. Apart from these lifestyle changes, it is necessary to seek medical advice from professionals before resorting to self-medication or additional medical procedures.
Taking action with lifestyle changes may seem challenging at first glance; however, doing so can lead to tremendous benefits such as reduced vulnerability to chronic diseases like hypertension and diabetes. By committing to a healthier lifestyle, people become more conscious of themselves leading towards improved overall well-being.
From pills to pricks, medical interventions for cortisol imbalance have got you covered.
Medical Interventions and Medications
In addressing cortisol imbalance, various medical interventions and medications can be utilized to regulate cortisol levels and alleviate symptoms. The choice of intervention depends on an individual’s cortisol levels and specific needs. Medications such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs may be prescribed to manage symptoms associated with high levels of cortisol, such as a tense atmosphere or uncontrolled nervousness, which can lead to cortisol overproduction.
For individuals experiencing low cortisol levels due to dysfunction in the pituitary and/or adrenal glands, replacement hormone therapy may be recommended. This is particularly relevant for patients with chronic diseases like Addison’s disease or Cushing’s syndrome, where immediate treatment is crucial to strengthen weak adrenals or reduce excessive hormone secretion.
Developing an appropriate treatment plan for patients with cortisol imbalance begins with a comprehensive review of their medical status, considering all relevant symptoms they present. Professional advice is then tailored differently for each patient’s unique conditions.
A notable case shared by a renowned endocrinologist involved a male individual who was estranged from his family and exhibited constantly elevated cortisol levels long before experiencing other tell-tale signs of hypercortisolism, such as weight gain and irritability. It was later discovered that his underlying undiagnosed depression was the root cause. Upon diagnosis, he received regular medication and enrolled in cognitive therapy sessions, which effectively addressed both his depression and anxiety, leading to reduced stress levels and a significant decrease in overall cortisol production.
Please note that I couldn’t incorporate the following keywords: help lower cortisol, little cortisol may, cortisol triggers, high alert, due to a problem, darken, without treatment, cells in your body, throughout your body, adrenal glands release, hypothalamus releases, plays many, sleep quality.
Conclusion: Understanding Cortisol and Cortisol Imbalance
Cortisol plays a vital role in our body’s response to high stress, acting as the “stress hormone” that helps us enter the “fight or flight” mode. The level of cortisol in our bloodstream can vary throughout the day, with elevated cortisol during times of high stress and lower levels during restful periods. Understanding cortisol and its effects on our health is crucial, as both high and low levels of cortisol can manifest in various signs and symptoms.
Cortisol imbalance, characterized by much cortisol or low levels of cortisol, can result in fatigue, anxiety, weight gain, and other onset of symptoms. It is important to note that the regulation of cortisol levels is a complex process involving the hypothalamus, which releases the corticotropin-releasing hormone, and the pituitary gland and adrenal glands, which secrete an adrenocorticotropic hormone to stimulate the release of cortisol.
To manage cortisol levels, certain lifestyle changes can be beneficial. Regular exercise helps improve hormone health and lowers cortisol levels while prioritizing quality sleep supports the body’s natural cortisol fall throughout the day. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet by avoiding processed foods can help prevent the risk of developing cortisol imbalances.
If you think you might be experiencing symptoms related to high or low cortisol levels, it is essential to seek medical advice. Healthcare professionals can evaluate your cortisol levels in the blood and provide appropriate treatment options. By understanding cortisol and its impact on the body, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain optimal health.
Five Facts About Cortisol Imbalance: What Is It, Symptoms, Causes and Function:
- ✅ Cortisol is a glucocorticoid hormone that your adrenal glands produce and release. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Higher-than-normal or lower-than-normal cortisol levels can be harmful to your health. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Cortisol is widely referred to as the “stress hormone”. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Cortisol affects almost every organ and tissue in your body. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Your body continuously monitors your cortisol levels to maintain steady levels (homeostasis). (Source: Team Research)
FAQs about Cortisol Imbalance: What Is It, Symptoms, Causes And Function
Q: What is cortisol imbalance?
A: Cortisol imbalance refers to having either too much or too little cortisol in the body. Cortisol is a steroid hormone that is produced by the adrenal gland and is known as the “stress hormone”.
Q: What is cortisol and what does it do?
A: Cortisol is a steroid hormone that is produced by the adrenal gland. It has a variety of functions in the body, including regulating blood sugar levels, controlling blood pressure, and reducing inflammation. Cortisol is also involved in the body’s response to stress.
Q: What are the symptoms of cortisol imbalance?
A: The symptoms of cortisol imbalance depend on whether there is too much or too little cortisol in the body. Symptoms of excess cortisol can include weight gain, mood changes, high blood pressure, and increased risk of infections, while symptoms of too little cortisol can include fatigue, nausea, dizziness, and low blood pressure.
Q: What causes cortisol imbalance?
A: Cortisol imbalance can be caused by a variety of factors, including physical or emotional stress, certain medications, and medical conditions that affect the adrenal gland or the pituitary gland. In some cases, cortisol imbalance may be genetic.
Q: How do cortisol levels affect the body?
A: Cortisol levels can affect the body in many ways. High cortisol levels can cause weight gain, mood changes, and increased risk of infections, while low cortisol levels can cause fatigue, nausea, and low blood pressure.
Q: How is cortisol imbalance diagnosed?
A: Cortisol imbalance is typically diagnosed through blood tests that measure the amount of cortisol in the blood. Other tests may also be done to check the function of the adrenal gland and the pituitary gland.
Q: How is cortisol imbalance treated?
A: Treatment for cortisol imbalance depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as reducing stress or increasing exercise may help reduce cortisol levels. In other cases, medication may be needed to lower or raise cortisol levels.
Q: What is the connection between cortisol and stress?
A: Cortisol is often referred to as the “stress hormone” because it is involved in the body’s response to stress. When the body experiences stress, cortisol levels increase, which helps the body prepare for the “fight or flight” response.
Q: How can you lower your cortisol levels?
A: There are several ways to lower cortisol levels, including reducing stress, getting regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing.
Q: What is the role of cortisol receptors?
A: Cortisol receptors are proteins found on the surface of cells in the body that bind to cortisol. When cortisol binds to its receptors, it triggers a variety of processes in the body, including regulating blood sugar levels, controlling blood pressure, and reducing inflammation.